The sky is hardly the limit when it comes to the innovative use of drones, which have taken the world by storm across diverse sectors. However, with the burgeoning use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), understanding the intricate tapestry of International Drone Regulations Overview is critical for operators and enthusiasts alike. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the complex framework of drone laws worldwide, steering through the multifaceted aspects of global UAV regulations.
Whether you’re capturing breath-taking aerial photography, engaging in precision agriculture, or delivering critical medical supplies, adhering to the established drone flying rules is paramount. The path to legal and responsible drone operation is paved with a sound grasp of international drone permits, ensuring your UAV ventures are compliant and set for success. Embark on a journey through the skies as we navigate the legalities that govern our increasingly drone-friendly airspace.
Understanding Global Drone Regulation Landscape
The tapestry of international drone laws has seen significant shifts and developments, shaped by advancements in technology and the growing ubiquity of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) across the globe. This intricate weave of regulations, heavily influenced by the invaluable insights from UAViators and key industry stakeholders, aims to create a harmonious balance within the airspace for both hobbyists and commercial enterprises. A closer look at the evolution of these regulations, their categorization, and the overarching emphasis on compliance and safety, divulges the profound impact they have on the era of unmanned aviation.
The Evolution of International Drone Laws
From their nascent stages, international drone regulations have undergone considerable metamorphosis. The database by UAViators planted the initial seeds in 2014, marking the beginning of a structured approach to understanding and navigating the burgeoning sphere of UAV legal requirements. Since then, an increasing number of aviation authorities have erected comprehensive frameworks to address the complexities presented by drone technology.
Categories of Drone Regulations: Recreational vs. Commercial
Amidst global aviation authorities regulations, a dichotomy has emerged distinguishing recreational from commercial drone use. Although recreational flying is generally governed by less stringent rules, encouraging more freedom for casual enthusiasts, commercial operations are tightly regulated. This differentiation is pivotal given the varying implications concerning privacy, airspace management, and potential commercial applications.
Drone Compliance and Safety Importance
Adhering to drone compliance standards is not merely a legal obligation, but a critical component for maintaining public safety and trust in UAV operations. Whether for leisure or business-related purposes, the importance of compliance cannot be overstated. It ensures the responsible use of drones, mitigates risks, and fortifies the credibility of UAV technology within both local and international contexts. It’s within this arena of regulation and conformity that the future of UAV ventures is sculpted, supported by an international drone regulations overview that continuously evolves to meet the demands of a sky teeming with potential.
Drone Laws by Region: Navigating Through Varied Airspace Restrictions
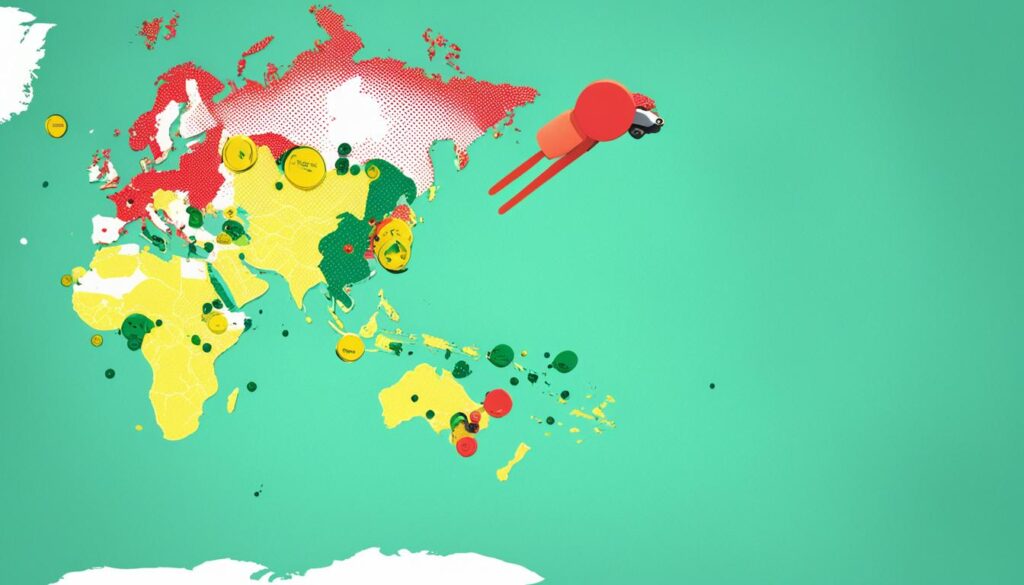
Understanding the airspace restrictions for drones is crucial for anyone involved in piloting UAVs, be it for leisure or commercial purposes. The complexity of drone laws by region requires thorough research and constant vigilance by drone operators to ensure compliance. With the international drone regulations overview ever-evolving, pilots must stay updated on the latest changes to avoid penalties and ensure safe operations.
When considering an international venture, drone enthusiasts and professionals alike must navigate a mosaic of regulations that vary dramatically from one jurisdiction to another. This landscape demands that operators not only understand global UAV standards but also respect local nuances that dictate how, where, and when they can fly their drones. To assist with deciphering this intricate tapestry, a resource such as the Second Source’s Drone Laws World Map becomes indispensable.
Representing over 170 countries through user-generated content, the map color-codes regions to symbolize their respective approach towards drone operation—a system designed to foster legal and safe flying.
To convey the complexity and diversity of these regulations, let’s look at a table that highlights the regional variance in drone legislation:
| Region | Status | Recreational Laws | Commercial Laws |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | Yellow | FAA registration required, guidelines for safe operation | Part 107 certification required for commercial use |
| Europe | Green/Yellow | Follow EASA regulations, drone registration | Specific permits for commercial operations depending on the country |
| Asia | Red/Yellow | Varies significantly by country, strict in certain areas | Often requires business permits and pilot registration |
| Africa | Red/Green | Many countries lack specific laws or have very liberal policies | Professional use usually requires detailed applications and permissions |
| Oceania | Yellow | Registration and adherence to CASA guidelines in Australia | Commercial operators need a Remote Piloted Aircraft Operator’s Certificate |
This regional insight into global UAV regulations underscores the importance of detailed understanding for both recreational flyers and commercial drone operators. The listed examples depict not only the breadth of regulatory environments encountered globally but also the spectrum of approaches to manage drone activity within different airspaces. Indeed, the ability to legally chart a course through these various airspace restrictions hinges on access to accurate, up-to-date information—a task made easier by the collaborative efforts of the international drone community.
Drone Flying Rules and Pilot Responsibilities Worldwide
With the increased ubiquity of drones in airspace around the globe, understanding and abiding by drone flying rules has never been more crucial for pilots. These rules are designed to ensure that UAVs are operated safely and responsibly, and adhering to them is not just a matter of courtesy but also of legal obligation. All pilots, regardless of where they are operating, must be acquainted with the comprehensive UAV legal requirements to ensure the safety of both people and property below.
General Global Guidelines for Safe Drone Flying
While specific UAV legal requirements may vary from one region to another, certain fundamental drone flying rules apply universally to guarantee safe flying practices. These include restrictions on flight altitude, avoiding risky maneuvers over populated areas, and ensuring the pilot maintains a visual line of sight with the drone at all times. Below is a summary of recommended international guidelines:
- Maintain a flight ceiling of 300-400 feet to mitigate the risk of conflicts with manned aircraft.
- Avoid flights over groups of people, public events, or densely populated areas to prevent potential injuries and breaches of privacy.
- Operate drones only while sober, as any impairment could jeopardize the safety of the flight.
- Ensure the drone remains within visual line of sight to maintain control and situational awareness.
- Restrict drone use to daylight hours or twilight periods with appropriate lighting conditions.
These guidelines serve as a cornerstone of responsible UAV operation and set the stage for safe integration of drones into the airspace.
The Importance of Following Local Drone Rules
Pilots must remember that while global guidelines offer a general framework for safe operation, local drone laws carry the force of law and must be followed meticulously. These laws have been tailored to address the specific needs and challenges of each airspace and may include additional pilot responsibilities such as registration, no-fly zones, and specific permissions for certain types of flights. It is incumbent upon pilots to familiarize themselves with these local regulations before conducting any drone operations.
For example, pilots operating in the United States must comply with the Federal Aviation Administration’s (FAA) Part 107, while in the European Union, the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) has its own set of standards. These regulatory bodies enforce rules that are critical to the safety and management of the airspace, and compliance is non-negotiable.
Overall, it is the pilot’s responsibility to ensure their knowledge of drone flying rules is up-to-date and comprehensive, respecting both the letter and the spirit of the laws that govern UAV usage. Doing so helps to reinforce the growing reputation of drone technology as a safe and valuable asset in both commercial and recreational contexts.
International Drone Permits: How to Secure Your Flight Legally
When it comes to embarking on international drone operations, one must navigate a labyrinth of legal requirements that vary significantly from country to country. Pilots need to be well-versed in international drone permits, familiarizing themselves with drone registration guidelines, and staying up-to-date with global UAV regulations to ensure full compliance and a trouble-free experience.
Obtaining Necessary Permits for International Drone Operation
Before you can enjoy the skies abroad, obtaining the right permits is crucial. This often means engaging with the destination country’s aviation authority to secure drone or pilot registration. Different countries may also require specific operator IDs or special flight permissions that reflect their unique concerns regarding airspace safety. This legal groundwork is pivotal in upholding the integrity and security of international airspace.
The Process of Applying for Drone Permits in Different Countries
Applying for drone permits is a process that demands diligence and a meticulous approach. It begins with a thorough investigation into the requisite permits for your drone’s destination. While some countries have embraced digital transformation, offering online registration platforms, others adhere to more traditional, direct-contact methods that could require face-to-face meetings or postal submissions.
Key components of a successful permit application typically include:
- A detailed application form, usually provided by the aviation authority.
- Proof of identity and, if necessary, proof of proficiency in operating a UAV.
- Evidence of drone insurance, where mandated, to cover potential liabilities.
The process can vary from instantaneous confirmations to weeks-long waiting periods, depending on the legal complexity and bureaucratic pace of the host country. Nevertheless, adherence to drone registration guidelines is a non-negotiable part of the process and a stepping stone to securing international drone operation clearance.

In conclusion, the key to international drone operation lies in early preparation, thorough research, and mindful observance of the destination country’s regulations. By demonstrating compliance and respect for global UAV regulations, drone operators not only ensure legal flights but also contribute to the safety and harmony of skies worldwide.
Drone Registration Guidelines Across Countries
Navigating through the intricacies of drone registration guidelines can be daunting, as the UAV legal requirements vary from country to country. With an ever-expanding tapestry of international drone regulations, it’s paramount for drone operators to comply with local mandates to ensure seamless international operations.
In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) mandates the registration of drones weighing over 0.55 pounds (250 grams). This process grants a unique identification number for each UAV, which must be visibly displayed on the aircraft. Conversely, in Europe, drone operators will familiarize themselves with a system where both the drone and the pilot require registration, promoting a more personalized accountability framework.
In anticipation of further regulatory refinement, the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) is moving towards tripartite legislation based on the operation’s risk profile. These categories extend from ‘open’ operations with low-risk drones, through ‘specific’ operations requiring additional authorizations, to ‘certified’ operations involving high-risk scenarios.
| Region | Drone Registration | Operator Registration | Identification Number Display Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Yes (drones over 0.55 lbs) | No | Yes |
| Europe (EASA) | Expected (starting June 2020) | Yes | Yes |
| Canada | Yes (drones over 250 grams) | Yes (pilot certificate required) | Yes |
| Australia | Yes (for commercial operations) | Yes | Yes |
| China | Yes | No | Yes |
It’s clear that the global trend emphasizes the discernible dichotomy between recreational and commercial drone use, with the latter commonly subjected to more stringent regulatory measures. As the distinctions of drone applications grow sharper and more complex, operators worldwide must remain vigilant, consistently updating their knowledge of changes in the international regulatory landscape.
International Drone Regulations Overview
In this comprehensive exploration of global UAV regulations, we delve into the multifaceted nature of drone laws that vary from one country to another. Through a comparative analysis, we aim to shed light on the international landscape governing UAV operations. Ever-changing technological advances and their implications on airspace regulation necessitate an ongoing examination of how nations are adapting their legal frameworks to ensure safety, privacy, and innovation.
Comparative Analysis of Global UAV Regulations
The world stage for drone legislation presents a mosaic of regulatory approaches, influenced by factors such as technological proficiency, safety concerns, and airspace usage. A comparative analysis of drone laws highlights these differences and underscores the importance for operators to acquaint themselves with these variations to fly compliantly.
Examining the Differing Approaches to Drone Regulation
From registration protocols to operational limitations, the spectrum of global UAV regulations is vast. The United States may offer a more lenient approach for recreational users, while nations in the European Union present a more intricate web of requirements designed to cater to a broad array of drone activities.
Case Studies: How Countries Implement International Drone Laws
Detailed case studies such as Germany’s requirement of flight permissions for heavier drones and Italy’s altitude and pilot identification regulations offer insight into how countries tailor their laws in response to the unique demands of drone technology and its integration into society.
“As drones continue to permeate various sectors of society, international regulations evolve in complexity; a cursory look affirms the need for ongoing vigilance and adaptation by UAV operators and regulators alike.”
Laws governing UAVs directly impact the operational capabilities of drone enthusiasts and professionals. Therefore, understanding the international drone regulations overview is not a mere academic exercise but a practical necessity for achieving global operational fluency.

Airspace Restrictions for Drones: An International Perspective
Ensuring the safety of our skies while fostering the growth of drone technology necessitates a deep understanding of international airspace restrictions. Regulations governing the operation of drones are pivotal in maintaining a balance between innovation and public safety. Today, countries around the world have set forth clear criteria that drone pilots must adhere to, especially when it comes to no-fly zones and height limitations.
Navigating No-Fly Zones and Restricted Airspaces
Central to the safe operation of drones is the identification and avoidance of no-fly zones. These areas, which are often heavily regulated to protect national security, public safety, and privacy, include locations such as airports, military bases, and government buildings. Pilots are obligated to stay aware of these restrictions to prevent unauthorized incursions and potential aerial conflicts. Country-specific aeronautical maps typically denote these zones, aiding operators in planning their flight paths accordingly.
Height and Proximity Limitations for Drones on a Global Scale
While no-fly zones dictate where drones may not fly, height restrictions determine how high they can ascend. A commonly accepted ceiling is 400 feet in uncontrolled airspace, a measure that helps to prevent interference with manned aircraft. Height restrictions for drones can vary by country and region, with additional rules often in place concerning the distance from people and structures these devices must maintain while airborne.
| Country | Max Height | Distance from Airports | Urban Area Flight | Special Permissions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 400 ft | 5 miles | No | Waivers available |
| Canada | 300 ft | 3.5 miles | With restrictions | SPC required |
| Australia | 120 m | 5.5 km | With restrictions | CASA approval |
| United Kingdom | 400 ft | 1 km | No | Permission from CAA |
Gaining permissions to operate within these restricted parameters often entails a rigorous application process, which may include providing detailed flight plans, the drone’s specifications, and the purpose of the operation. Understanding the procedural nuances for each jurisdiction is vital for securing the necessary approvals to fly legally and safely.
Community-Driven Updates on Drone Law Changes
The dynamic world of drone law updates is significantly influenced by the active participation of the drone community. Knowledge-sharing platforms and online forums are at the forefront of circulating the latest UAV legal requirements and changes in legislation. With the collective efforts of enthusiasts and professionals alike, these community-driven drone regulations contribute to a more informed and compliant drone-operating environment worldwide.
Representing an invaluable resource, the community’s input offers a real-time perspective on the practical implications of flying drones within the current legal framework. This collaboration is not only essential in fostering a responsible drone culture but also acts as an engine driving the advancement of regulations that address both innovation and safety concerns.
“Staying abreast of the latest regulatory changes is a responsibility shared by the entire drone community. Our collective input has the power to shape a safer airspace for everyone.” – Drone Enthusiast Forum contributor
Below is a table summarizing some recent cooperative efforts that have successfully impacted drone law updates in various regions:

| Region | Community Contribution | Resulting Action |
|---|---|---|
| North America | Submission of safety incident reports | Implementation of new safety protocols |
| Europe | Feedback on drone registration processes | Simplification of registration procedures |
| Asia-Pacific | Forum discussions on urban airspace integration | Pilot programs for urban drone delivery services |
| Africa | Sharing of data on drone use in agriculture | Adoption of drones for crop monitoring |
This collective approach not only empowers pilots by giving them a voice in the regulatory process but also helps authorities in crafting measures that truly reflect the community’s needs and experiences. The symbiotic relationship between drone operators and legislators through forums and discussions paves the way for an evolving regulatory landscape that aligns with technological growth and public safety.
Global UAV Regulations and the Role of Aviation Authorities
The intricacies of the global landscape for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are largely shaped and enforced by international and regional aviation authorities. These regulatory bodies, including the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States and the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) in Europe, are the cornerstone of UAV legal requirements and compliance, wielding vast influence over the implementation of aviation authorities regulations that oversee the burgeoning drone industry.
Around the World with FAA, EASA, and Other Aviation Bodies
While the FAA and EASA are by far the most prominent, various other aviation authorities across the globe contribute to the complex tapestry of international drone regulations. Each body adapts its rules and guidelines to suit its airspace, balancing the need for innovation with safety and privacy concerns. From the issuance of pilot certifications to specifying operational criteria, these institutions are integral in shaping the future of UAV operations.
Understanding the Enforcement of Drone Laws by Authorities
Enforcement is a critical aspect of aviation authorities regulations, ensuring that UAV operators adhere to set legal requirements. Variable enforcement mechanisms reflect diverse operational contexts, with some authorities depending on technological solutions such as remote identification systems, while others conduct on-site inspections and monitoring. The successful enforcement of these regulations is pivotal in maintaining a safe and legally compliant airspace, fostering trust in the UAV industry’s commitment to responsible flying practices.
Drone Compliance Standards: Ensuring International Operation Conformity
As the skies grow increasingly populated with drones, the importance of establishing strict drone compliance standards is paramount for safe and reliable international operations. Ensuring that these standards are met requires a concerted effort from regulatory bodies, manufacturers, and drone operators to achieve international operation conformity.
The Significance of Compliance in Global Drone Operation
Compliance is the cornerstone of international drone usage. Adhering to established guidelines not only facilitates safer skies but also promotes legal cross-border operation and fosters trust among nations. It’s essential that all parties involved understand the gravity of adhering to these compliance measures to uphold the integrity of standardization in drone regulations.
Standardization Efforts in Drone Regulations
As countries around the world grapple with the complexities of drone management, the European Union (EU) has been at the forefront of standardization efforts in drone regulations. This is evident in their push towards a harmonized regulatory framework which addresses the challenges of UAV operation while still fostering innovation. Observance of these emerging global standards is critical for ensuring a seamless integration of UAV activities across international boundaries.
Legal Implications of Non-Compliance with Drone Regulations
The burgeoning use of drones across numerous industries and for recreational purposes has engendered a complex legal landscape punctuated by stringent rules and regulations. Non-compliance with drone regulations carries significant legal implications, which underscore the importance of adhering to the laws established by regulatory bodies. One of the primary concerns for drone operators should be understanding local and international laws to avoid contravening airspace sovereignty, compromising public privacy, and potentially incurring liabilities.
Penalties for Non-Compliance can vary widely, often determined by the gravity of the offense and the laws of the specific jurisdiction. Some common consequences include:
- Fiscal fines, which may escalate with repeated offenses
- Confiscation of drones or related equipment
- Revocation of the pilot’s operating license
- Potential criminal charges leading to trials and possible incarceration
Below is an illustrative table, amalgamating data on the various penalties which have been enforced in different regions for non-compliance with drone regulations:
| Region | Violations | Penalties |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Flying without proper authorization | Fines up to $27,500 for civil penalties, over $250,000 for criminal |
| European Union | Violating privacy laws | Severe fines and potential for legal prosecution |
| Canada | Flying in restricted airspace | Fines up to CAD $25,000 and/or seizure of the drone |
| Australia | Endangering manned aircraft | Penalties including fines and possible jail time |
The consequences of non-compliance with drone regulations are not solely punitive but can also influence legislative amendments, often resulting in more restrictive flying conditions for all operators. Instances of non-compliance fuel public skepticism, which in turn pressures legislators to impose harsher regulations.
Given the ever-evolving nature of drone technology and its applications, regulatory frameworks are constantly under review. This dynamic necessitates a vigilant approach to compliance by operators to mitigate the legal and societal impacts.
Ultimately, understanding and obeying drone laws is of paramount importance—it ensures the liberty of airspace for future drone innovations, maintains public trust, and most importantly, shields operators from the detrimental legal implications that can arise from non-compliance with drone regulations.
Drone Insurance Requirements for International Flights
Navigating the skies with a drone internationally does not only require a solid understanding of international drone permits but also a thorough grasp of drone insurance requirements. Many countries mandate that drone operators carry proof of insurance, especially liability coverage, as a condition for granting permission to fly. Just as having a passport and visa are critical for international travel, securing comprehensive drone insurance coverage is essential for legal and financial protection during international drone operations.
Liability insurance, in particular, is a common focus for international regulators. This coverage is designed to protect against claims resulting from injuries and property damage to third parties caused by your drone activities. Coverage levels may vary from one country to another, and understanding these nuances is crucial.
- Research and compare insurance policies that meet the unique requirements of your destination country.
- Ensure your insurance coverage includes the necessary liability protection for the regions you will operate in.
- Keep your insurance documents accessible, as proof of insurance may be required upon entry or flight approval.
Failure to comply with local drone insurance requirements can lead to denied flight permissions, fines, or other legal complications that underscore the importance of adequate preparation before embarking on international drone flights. It is not merely about fulfilling a requirement – it’s about ensuring peace of mind as you fly, capturing the world from above, secure in the knowledge that you are fully protected.
Conclusion
The world of International Drone Regulations Overview is as dynamic as it is diverse. For both hobbyists and professional drone operators, the spectrum of UAV rules presents a critical roadmap to navigating the skies legally. By dissecting the complexities of global UAV laws, this article has provided readers with essential insights into the multifaceted nature of complying with these regulations. The overarching message is clear: diligent research, preparedness, and adherence to regulations are the keys to ensuring drone operation compliance.
The intricate web of international standards and localized regulations poses a constant learning curve. However, it also offers an unprecedented opportunity for drone enthusiasts and commercial pilot enterprises to operate in an informed and conscientious manner. As the drone industry continues to soar, the commitment to legal compliance not only fosters safe flights but also catalyzes the advancement of UAV technologies and their applications across different sectors—effectively expanding the horizons of aerial innovation.
Armed with the knowledge from this comprehensive exploration of drone policies, operators have the capacity to fluidly intertwine their aerial ambitions with the jurisdictional tapestries that govern them. Undoubtedly, the quest for harmonization of drone laws and the proactive participation of the drone community will continue to shape the framework of safe and compliant drone integration into the airspace of tomorrow.
FAQ
What is an International Drone Regulations Overview?
The International Drone Regulations Overview encompasses the various legal frameworks, requirements, and guidelines imposed by different countries to govern the use of drones or UAVs within their airspace. It provides information on the diverse set of rules pertaining to drone registration, operation, safety standards, and compliance for both recreational and commercial uses worldwide.
How do drone laws differ between recreational and commercial use?
Recreational drone laws are generally less restrictive and are designed for hobbyists who fly drones for personal enjoyment. Commercial drone laws, on the other hand, are more stringent and apply to operations that involve any form of business activity or financial gain. These may include requirements for pilot certification, higher levels of insurance, and stricter operational guidelines.
Why is it important to comply with drone safety and compliance standards?
Complying with drone safety and compliance standards is crucial for ensuring the safety of both the drone operators and the general public. It helps in preventing accidents and incidents that could lead to injury, damage to property, or interference with other airspace users, including manned aircraft. Compliance also upholds legal requirements and can prevent legal penalties and loss of equipment.
What are the typical drone flying rules that apply across various countries?
Typical drone flying rules that are commonly advised globally include maintaining a safe distance from people and sensitive areas, flying at a maximum height of around 300-400 feet to avoid manned aircraft, ensuring the drone remains within the visual line of sight, not flying under the influence of alcohol or drugs, and only operating the drone during daylight hours unless authorized for night flying.
How can one secure international drone permits for legal flight operations?
To secure international drone permits, operators must research the specific requirements of the country they intend to fly in. This may involve registering with the local aviation authority, applying for necessary permits, and submitting any required documentation. This process may vary from completely online submissions to interactions with local aviation bodies.
Are there differences in drone registration guidelines across countries?
Yes, there are significant differences in drone registration guidelines across countries. Some countries may require the drone itself to be registered, while others require the pilot to be registered and provided with an identification number. The upcoming European drone regulations, for instance, will introduce three categories of operations to standardize drone legislation across member states.
What are some examples of the approaches countries implement for international drone laws?
Approaches to drone regulations vary extensively. For instance, Germany requires permissions for drones weighing over 11 pounds and for night flights. Italy enforces altitude restrictions and mandates pilot identification. These differing approaches reflect each country’s attempt to balance the benefits of drone technology with concerns of safety, security, and privacy.
Why is it important to navigate no-fly zones and understand airspace restrictions for drones?
It’s essential to navigate no-fly zones and understand airspace restrictions to prevent unauthorized drone flights in areas that could compromise safety, national security, or privacy. This includes avoiding flights near airports, military bases, critical infrastructure, and other sensitive areas. Flying in restricted areas without permission can lead to legal actions including fines and criminal charges.
How do aviation authorities like the FAA and EASA regulate drone use?
Aviation authorities such as the FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) in the United States and EASA (European Aviation Safety Agency) in Europe are responsible for creating and enforcing drone regulations within their respective jurisdictions. These authorities set the standards for drone operation, pilot certification, airspace rules, and conduct surveillance and enforcement to ensure compliance with the regulations.
What are the potential legal implications of not adhering to drone regulations?
Non-adherence to drone regulations can lead to a range of legal implications including fines, confiscation of the drone, or even criminal charges depending on the severity of the violation. Operators may face additional sanctions from aviation authorities, and consistent non-compliance could influence tighter restrictions on drone use for all operators.
What are the requirements for drone insurance when flying internationally?
When flying drones internationally, operators are often required to have liability insurance to cover any damage or injury their drone might cause. The specific insurance requirements can vary, but they often mandate a minimum level of coverage and may require the insurance to be valid in the country where the drone will be operated.
Leave a Reply